The dsRNA contamination and its risks in the mRNA vaccine, From BioNTech Patent.
I newly discovered BioNTech patent regarding a relationship between GTP/UTP concentrations and dsRNA.
I newly discovered BioNTech patent regarding a relationship between GTP/UTP concentrations and dsRNA, and hence I would like to report this here.
I previously reported BioNTech patent US20230183769A1 regarding the ATP and CTP concentrations in connection with the Process 2 (ref. 1). Reference links will be attached at the end of this post.
Masterpiece of BioNTech & Pfizer
Regarding BioNTech patent US2023/0183769A1 I previously posted, which admittedly increases the residual DNA, I would like to emphasize another point here. Please compare the descriptions of the patent and the EMA document as reproduced below. The two documents say almost same thing, but ''something'' is missing from
The filing date of the above patent is September 1, 2021. To briefly summarize the above patent, by adjusting the ATP and CTP concentrations, BioNTech increased the yield of RNA, decreased the amount of dsRNA contamination, and increased the amount of residual DNA contamination. That is, their vaccine is a product full of compromises.
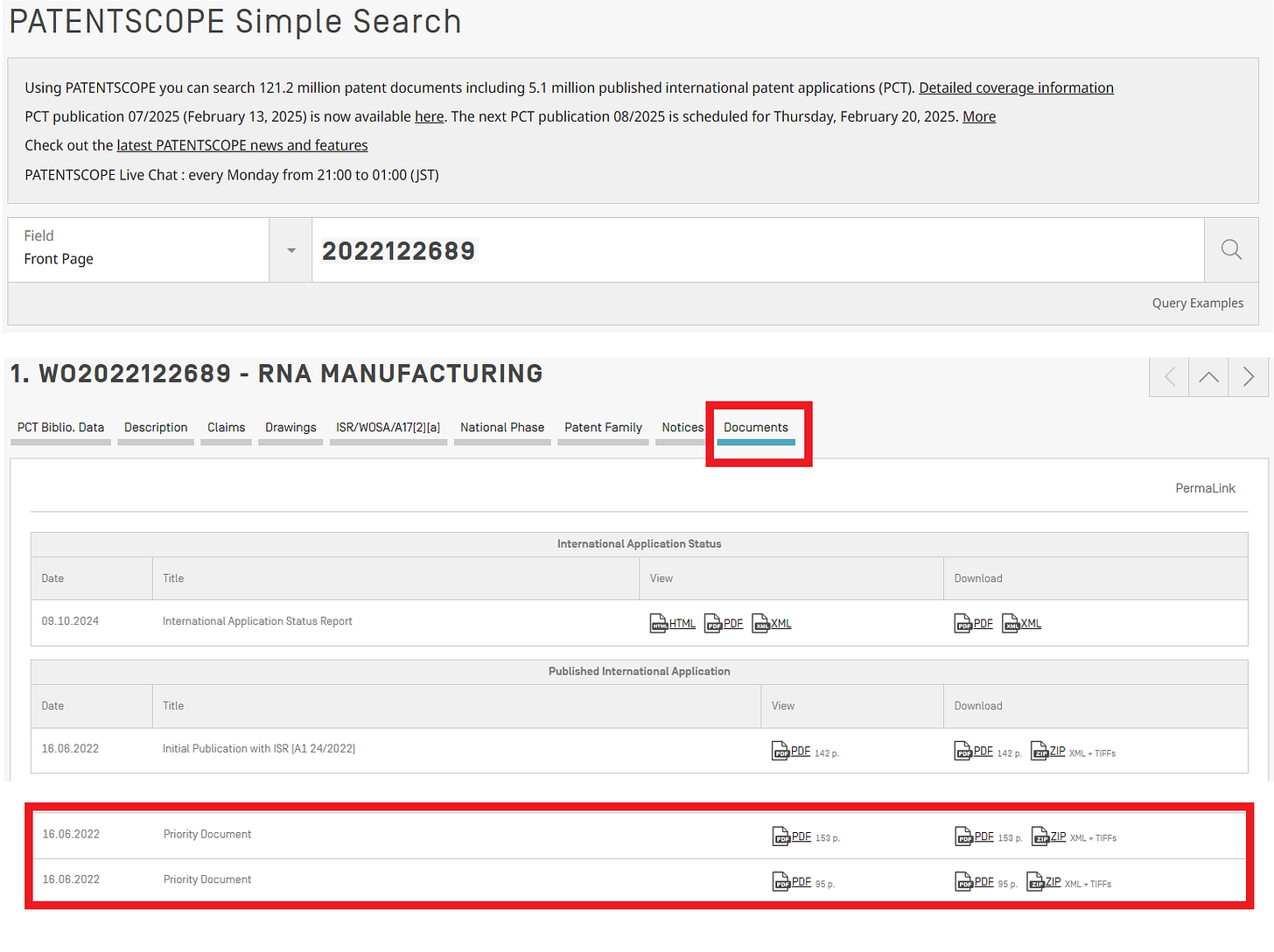
The patent publication number this time is WO2022122689A1 (ref. 2).
The patent filing date is December 7, 2021, and the patent publication date is June 16, 2022. This would be a successor patent to the above patent US20230183769A1 (=filing date: September 1, 2021).
This patent is based on two provisional applications filed in the United States. The main contents of WO2022122689 are also disclosed in the Provisional Application No. 63/123465. Therefore, the actual filing date of WO2022122689 is deemed to be December 9, 2020.
The Provisional Application No. 63/123465 can be obtained by entering "2022122689" in the WIPO patent search and selecting "Priority Documents" from the "Documents" section.
https://patentscope2.wipo.int/search/en/search.jsf
The family of this patent is here.
This patent have not discovered for about two years after its publication, and thus this shows how difficult it is for the public outside the patent field (even me) to search for the specific patent.
This patent discloses contents that support the contents of the EMA document (ref. 3) and that are along with the paper including Katalin Karikó as the one of authors (ref. 4).
Furthermore, this patent also mentions the production of abnormally long mRNA due to an "RNA backfolding", which is not disclosed in those documents. Further verification of the "RNA backfolding" will be required.
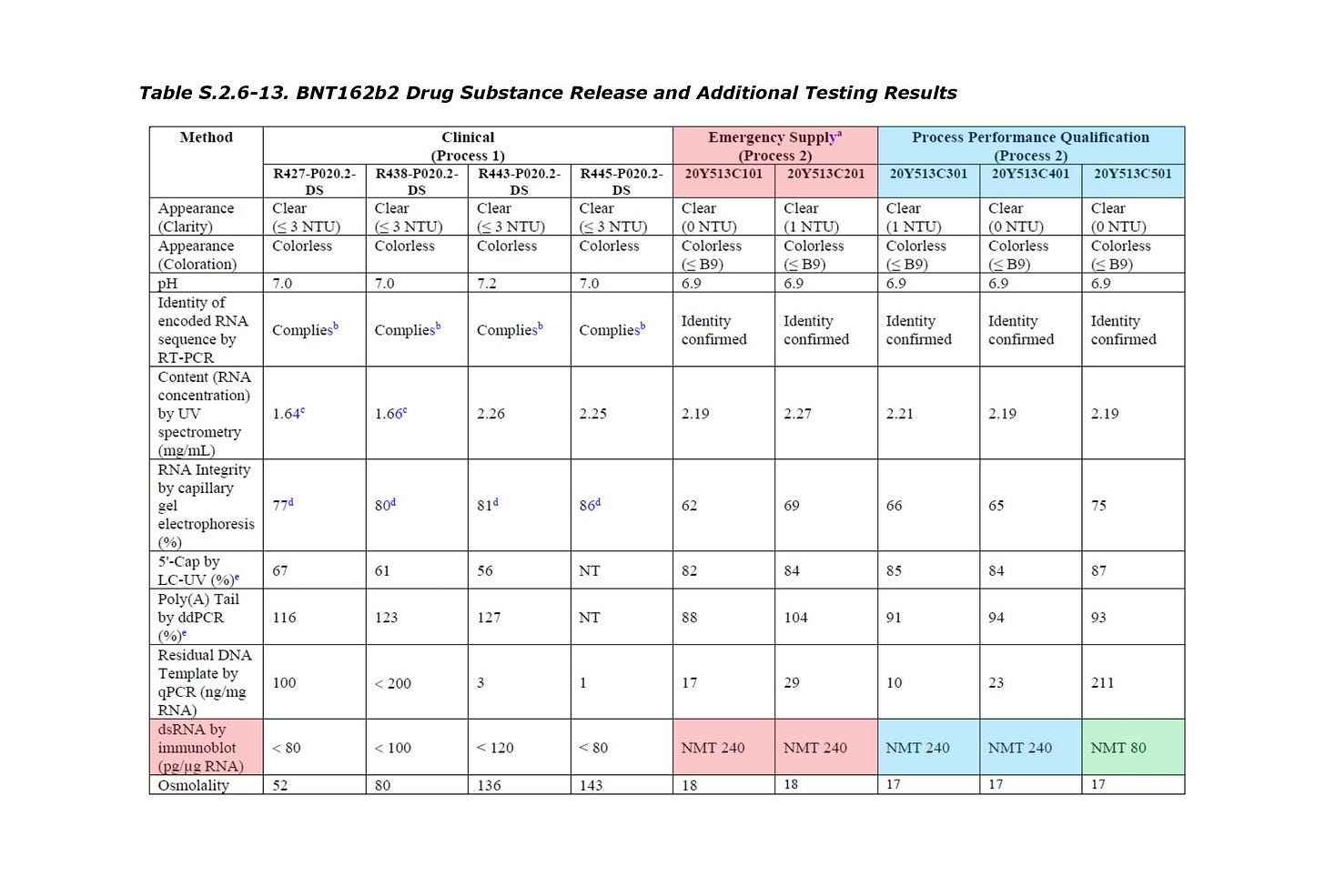
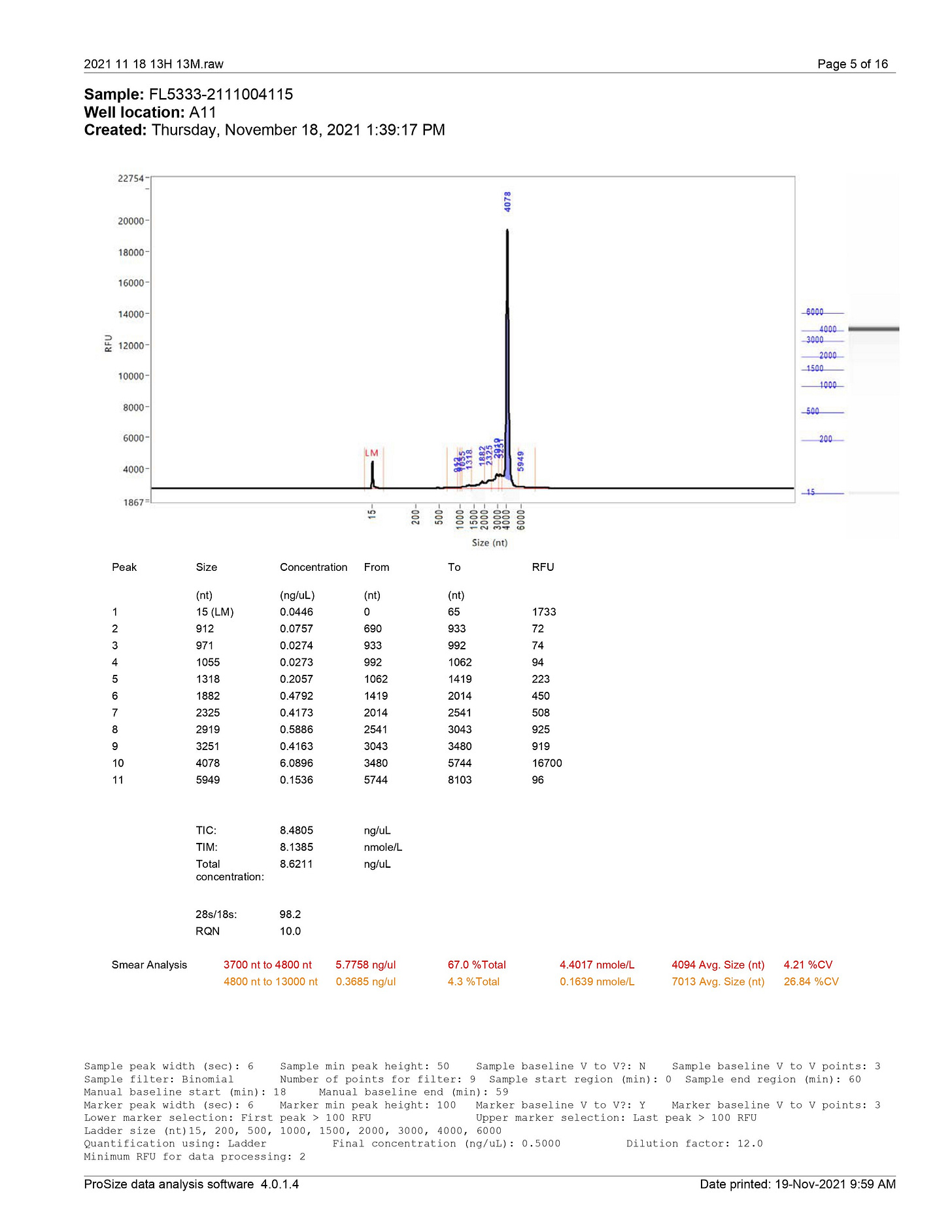
This patent primarily teaches risks associated with the dsRNA and a method for reducing the dsRNA. Note that the mRNA vaccine with a relatively large amount of dsRNA contamination had been actually introduced into the human body in the early stages (Emergency Supply, etc.), as shown in the attached Table. S 2.6-13.
Surprisingly, the Table 5-1 attached in the patent is the completely same as the Table S. 2.4-1 attached in the EMA document (see attached image), and therefore, first of all, the relevant parts of the EMA document are picked up as noteworthy points.
The tagline "safe and effective" has been used for the mRNA vaccine since its introduction. Please think about why it was necessary to reduce the amount of dsRNA contamination after its introduction, even though the mRNA vaccine is "safe and effective," through this post.
Regarding the relationship between the GTP and UTP concentrations and the dsRNA, the EMA document states as follows:
For the current process, linearized plasmid DNA template was chosen for scalability in order to feasibly supply the current vaccine needs. The GTP and N1-methylpseudo UTP starting concentrations are controlled at a low target and these solutions are delivered as bolus feeds. These ribonucleotides were chosen to be limiting reagents to aid in capping and to reduce potential dsRNA impurities. The 5’-cap is in stoichiometric excess to the GTP to enable the preferential incorporation of the 5’-cap as the first addition to the RNA transcript. Dditionally, controlling the N1-methylpseudo UTP concentration in the reaction is proposed to reduce the dsRNA impurities.
That is, it is understood that BioNTech (Pfizer) set the GTP and UTP concentrations in relatively low values to reduce the amount of dsRNA contamination. The production mechanism of the dsRNA and its composition are unknown here.
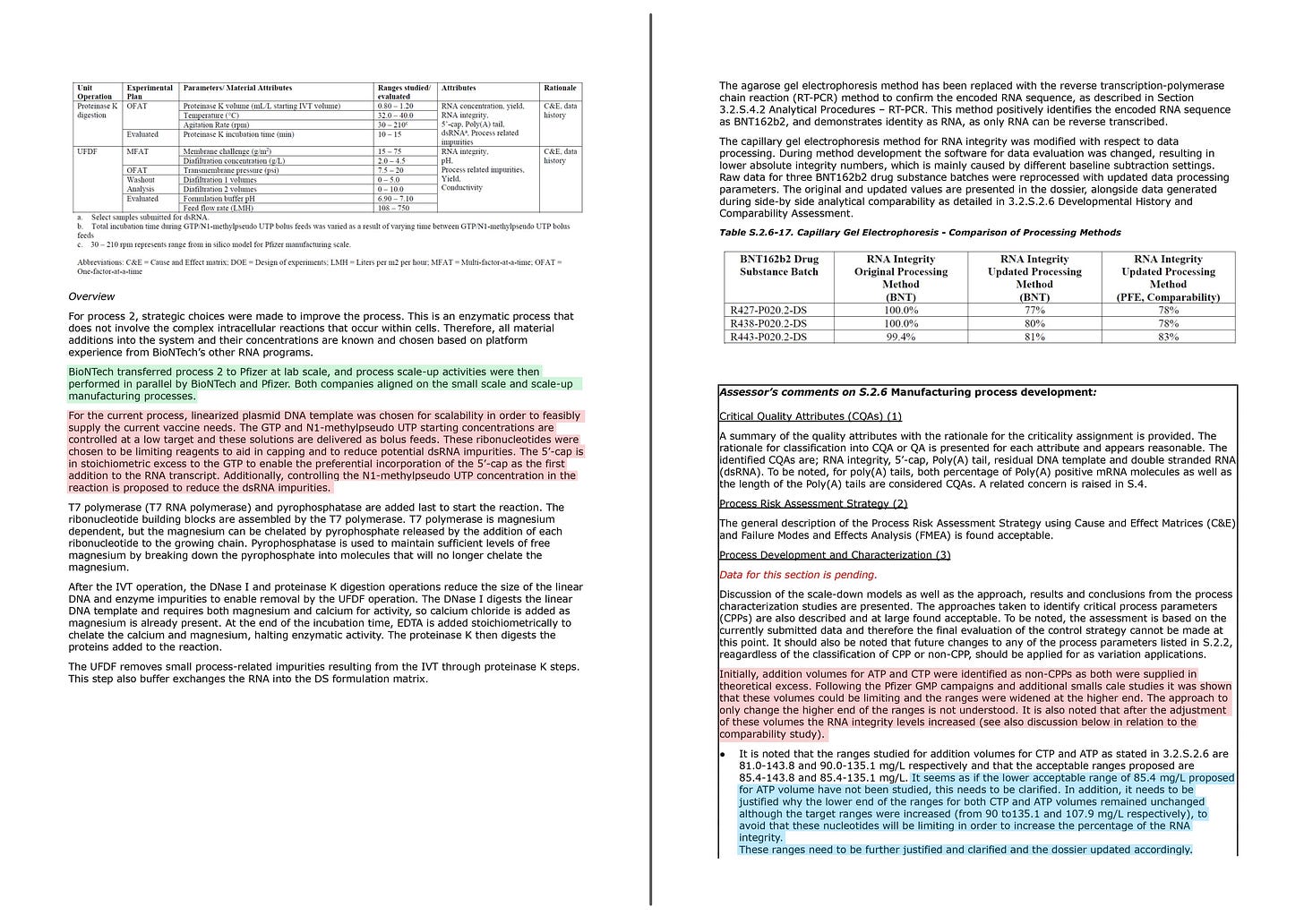
Note that the EMA has sharply pointed out to BioNTech (Pfizer) for not adequately explaining the lower limits of the ATP and CTP concentrations.
Initially, addition volumes for ATP and CTP were identified as non-CPPs as both were supplied in theoretical excess. Following the Pfizer GMP campaigns and additional smalls cale studies it was shown that these volumes could be limiting and the ranges were widened at the higher end. The approach to only change the higher end of the ranges is not understood. It is also noted that after the adjustment of these volumes the RNA integrity levels increased (see also discussion below in relation to the comparability study).
・It is noted that the ranges studied for addition volumes for CTP and ATP as stated in 3.2.S.2.6 are 81.0-143.8 and 90.0-135.1 mg/L respectively and that the acceptable ranges proposed are 85.4-143.8 and 85.4-135.1 mg/L. It seems as if the lower acceptable range of 85.4 mg/L proposed for ATP volume have not been studied, this needs to be clarified. In addition, it needs to be justified why the lower end of the ranges for both CTP and ATP volumes remained unchanged although the target ranges were increased (from 90 to135.1 and 107.9 mg/L respectively), to avoid that these nucleotides will be limiting in order to increase the percentage of the RNA integrity.
These ranges need to be further justified and clarified and the dossier updated accordingly.
The main points of this invention (patent) are extracted from the descriptions of the Claim section (Claims 1 to 3 are described here for convenience), and they are specifically as follows:
(A) This is a method of producing a composition comprising RNA having a reduced double-stranded (ds) RNA content.
(B) The starting concentration of UTP, or a functional analog thereof, is lower than the starting concentration of CTP and/or ATP, or a functional analog thereof.
(C) The method comprises supplementing the reaction mix during the course of the transcription reaction with a composition which comprises UTP, or a functional analog thereof, and is substantially free of CTP or ATP, or a functional analog thereof.
These points (A) to (C) are consistent with the disclosures in the EMA document. And these specific conditions are disclosed in the Table 5-1 of the patent which is identical to the Table S. 2.4-1 of the EMA document.
Regarding the dsRNA, the "Summary" section and the "DS RNA Contaminants" section in the patent specification are reproduced below. These descriptions are very interesting, and thus please read carefully.
Summary
[3] RNA transcribed in vitro (e.g., by T7 RNA Polymerase (RNAP)) can contain aberrant products, including at significant levels. Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is proposed that some or all such products can be generated by unconventional activity of a utilized RNAP. One such aberrant product is dsRNA, which can prove particularly problematic, for example in light of its propensity to induce inflammatory cytokines and/or to activate immuno-effector proteins which, among other things, can lead to inhibition of protein synthesis. dsRNA is typically the major contaminant of in vitro RNA transcription reactions.
DS RNA Contaminants
[165] As known in the art, during synthesis of mRNA by a transcription reaction, e.g., in vitro transcription (IVT), e.g., using T7 RNA polymerase or another RNAP, significant amounts of aberrant products, including double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) (e.g., involving hybridization of distinct RNA molecules) are produced due to unconventional activity of the enzyme. dsRNA has been shown to induce inflammatory cytokines and activates effector enzymes leading to protein synthesis inhibition.
[166] As noted herein, dsRNA contamination of in vitro transcription reactions can be problematic. At least two different types of dsRNA contaminants have been described: (i) short dsRNAs in which antisense fragments base pair with the RNA transcript of interest (e.g., an mRNA product) and (ii) nearly full-length dsRNAs. Both can be generated by promotor dependent or promotor-independent RNAP (e.g., T7) activity; some maybe influenced by termination sites within the template.
[167] Without wishing to be bound by theory, we note that various mechanisms have been proposed for production of dsRNA during in vitro transcription. For example, in some instances, short RNA transcripts (e.g., about 5 to about 11 nt long) may be generated when an enzyme that has initiated synthesis aborts before completing the transcript and may then prime transcription of a complementary strand. Alternatively or additionally, RNA backfolding might lead to prolonged transcription, even generating extra-long (potentially twice the size, or even more) transcripts. Still further alternatively or additionally, reinitiation of transcription at certain open template structures might lead to transcription to generate an antisense strand. Reports have also suggested that template termination sites may influence production of dsRNA.
[168] The present disclosure provides, among other things, technologies whereby dsRNA is reduced in RNA preparations. For example, in some embodiments, dsRNA present in an RNA preparation prepared according to the present disclosure is reduced relative to that present in an RNA preparation prepared, for example, using equimolar amounts of ATP, GTP, CTP and UTP.
Noteworthy main points are as follows:
Main point 1:
dsRNA as the major contaminant (aberrant product) has been shown to induce inflammatory cytokines and activates effector enzymes leading to protein synthesis inhibition.
Main point 2:
(i) Short dsRNAs in which antisense fragments base pair with the RNA transcript of interest (e.g., an mRNA product) and (ii) nearly full-length dsRNAs. Both can be generated by promotor dependent or promotor-independent RNAP (e.g., T7) activity; some maybe influenced by termination sites within the template.
Main point 3:
Short RNA transcripts (e.g., about 5 to about 11 nt long) may be generated when an enzyme that has initiated synthesis aborts before completing the transcript and may then prime transcription of a complementary strand.
Main point 4:
RNA backfolding might lead to prolonged transcription, even generating extra-long (potentially twice the size, or even more) transcripts.
As you may have already noticed, the descriptions relating to the dsRNA in this patent follow (copy) a part of the paper of Katalin Karikó (ref. 4).
First, in Conflicts of Interest, this paper mentions as follows:
Conflicts of Interest
All authors are employees of BioNTech RNA Pharmaceuticals, a company that develops mRNA-based therapies. M.B. and K.K. have a pending patent application titled “Methods for Providing Single-Stranded RNA” for the technology presented in this paper.
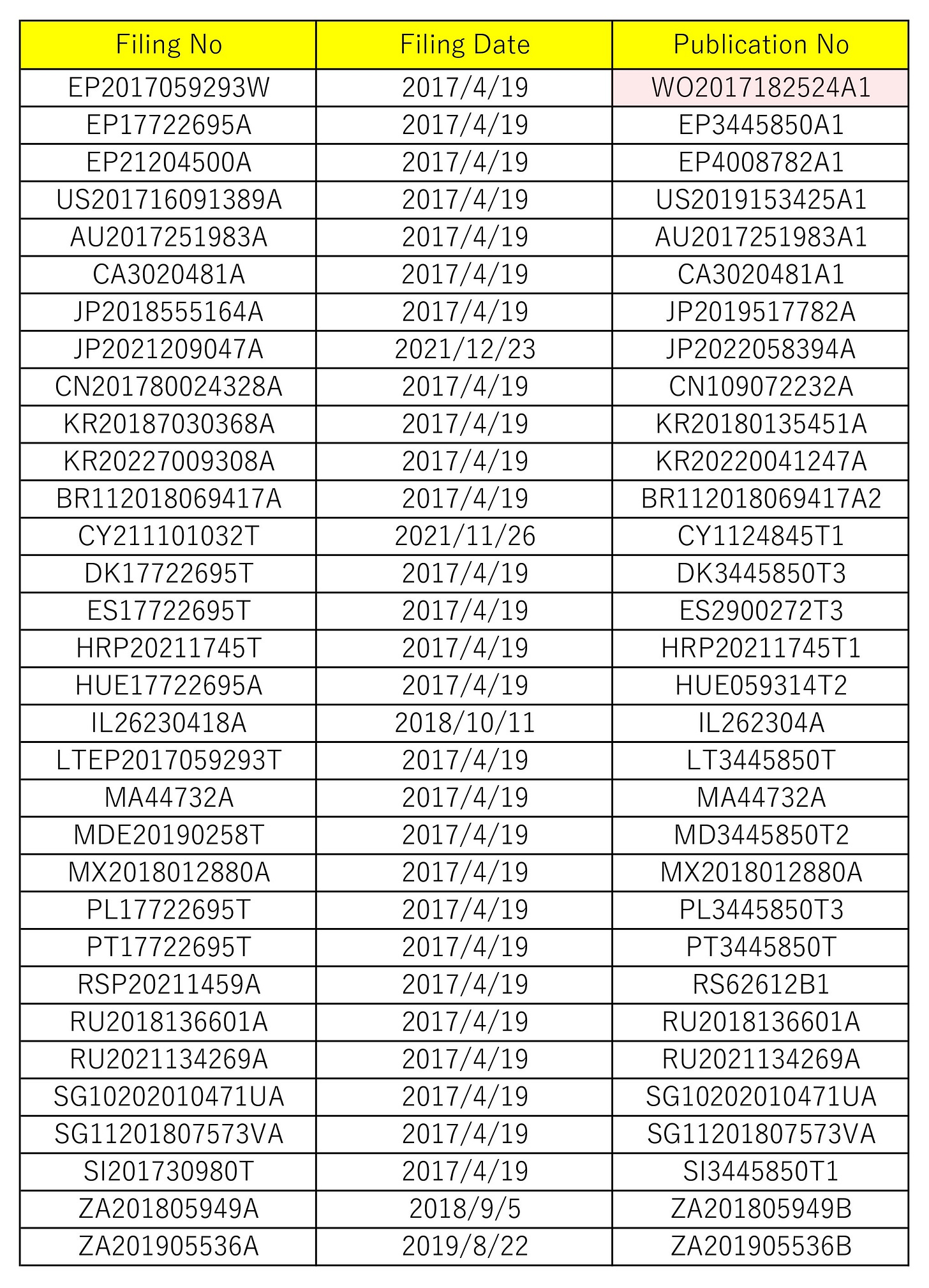
The BioNTech patent mentioned here is WO2017182524A1 (ref. 5), which discloses content different from this time patent.
The patent family of WO2017182524A1 is as attached. This patent information is for reference only (that is, information provision), and an explanation for this is omitted here.
The introduction section of this paper is reproduced below.
Introduction
In recent years, in vitro-transcribed (IVT) mRNA for research and therapeutic applications has gained tremendous interest (reviewed by Sahin et al.1). The simplicity of the approach to synthesize almost any protein in vitro or in vivo by delivering the encoding IVT mRNA makes it very appealing. Phage RNA polymerases, including T7 RNA polymerase (T7RNAPol), transcribe the RNA with high fidelity from a DNA template containing the corresponding promoter.2 However, during the initiation of transcription, 5- to 11-nt-long RNA by-products are generated as the enzyme aborts the synthesis with a certain probability.3, 4 Considering that the T7RNAPol also has an obscure RNA-dependent as well as template-independent RNA polymerase activity,5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 the short abortive RNA fragments and the 3′ end of the full-length RNA can prime complementary RNA synthesis from the primary transcripts that leads to the generation of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) contaminant. Recently, a promoter-independent transcription of full-length anti-sense RNA has been also reported as a novel mechanism of dsRNA generation in T7RNAPol-driven IVT reaction.13
The nuclei of human cells contain dsRNA that plays a role in natural biological processes;14, 15 however, when dsRNA enters the cells, from the extracellular milieu into their endosome or cytoplasm, it is sensed as a viral invader. All cells are capable of responding to dsRNA through sensors and effectors. Activation of dsRNA-dependent enzymes, such as oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS), RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR), and RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR), results in the inhibition of protein synthesis. In addition, stimulation of the dsRNA sensors, e.g., Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I), and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5), leads to the secretion of different cytokines, including type I interferons, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (reviewed by Hartmann16). Therefore, the elimination of dsRNA from the IVT mRNA is crucial to improve translation of the administered mRNA and to limit induction of cytokines, whether the mRNA products are intended for in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo applications and to be delivered by electroporation or in formulation.
These disclosures correspond to the above Main points 1 to 3 of the patent. For example, regarding the Main point 2 of the patent, the promoter-dependent transcription seems to correspond to the papers of "5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12" cited in the paper, and the promoter-independent transcription seems to correspond to the paper of "13" cited in the paper.
Main point 2:
(i) Short dsRNAs in which antisense fragments base pair with the RNA transcript of interest (e.g., an mRNA product) and (ii) nearly full-length dsRNAs. Both can be generated by promotor dependent or promotor-independent RNAP (e.g., T7) activity; some maybe influenced by termination sites within the template.
However, this paper lacks a description regarding the Main point 4.
Main point 4:
RNA backfolding might lead to prolonged transcription, even generating extra-long (potentially twice the size, or even more) transcripts.
The RNA backfolding may be a novel knowledge revealed by BioNTech in this patent. From those descriptions, it is understood that BioNTech was aware that an abnormally long mRNA (that is, a mysterious mRNA that is more than twice the length of the spike mRNA) was to be produced.
Is the RNA backfolding intended to be "Template Strand Switching by T7 RNA Polymerase" (ref. 6) or a similar phenomenon to this?
According to "Template Strand Switching", in the case of BioNTech plasmid DNA, T7 RNA Polymerase switches from the reverse ORF to the forward ORF, forming a long mRNA encoding both ORFs.
A mysterious mRNA shorter than the Spike mRNA and a mysterious mRNA longer than the Spike mRNA have been actually detected according to the TGA document of Pfizer (ref. 7) and the study from Mr. McKernan (ref. 8).
According to the TGA document, there are certainly long mRNAs in a range between 4800nt to 13000nt (average: 7013nt).
In addition, BioNTech's reverse ORF has a prion motif-rich structure (silk-like structure) containing 23 GxxxG-motifs and 144 G4-motifs (ref. 9). This image was borrowed from Mr. McKernan's Substack, and I added annotations.
The ORF11 is the forward ORF and the ORF19 is the reverse ORF. The spike mRNA is synthesized from the reverse ORF19 as a template. It is extremely likely that the long mysterious mRNA encodes the reverse ORF19 having the prion motif-rich structure.
FYI: The ORF sequences can be obtained from the following tool.
ORFfinder Home - NCBI (nih.gov)
Please enter and submit "OR134577" as the accession number.
See also my post on Twetter (X).
The reason why BioNTech (Pfizer) does not disclose an RNAseq result to this is probably because they do not want this mysterious mRNA to be analyzed in detail.
I could not extract any suitable papers regarding the "RNA backfolding," and therefore, I would like to request further verification for this issue, including the verification to this patent, by volunteers. The description of the "RNA backfolding," etc., will be one of strong evidences that BioNTech was aware of the risks of the mysterious long mRNAs.
This patent discloses specific experimental method examples for reducing the dsRNA after para [0349]. Here I pick up some descriptions that interest me.
Example 1: Exemplary IVT reactions limiting UTP or UTP and ATP in the transcription reaction can reduce generation of dsRNA content
[350] The present example demonstrates an exemplary fed-batch procedure to enhance capping efficiency and/or manipulate the amount of double stranded RNA (dsRNA) content generated during an in vitro transcription (IVT) reaction. In some embodiments, dsRNA is produced by backward transcription (e.g., 3’ to 5’ direction). In some embodiments, limiting NTPs needed for transcription starting from the 3’ end minimizes this effect. The present example specifically demonstrates that limitation of UTP in vitro transcription reactions, can reduce formation of dsRNA, and can be particularly useful for production of transcripts that may include a polyA sequence such as, for example, a polyA tail. Without wishing to be bound by theory, we propose that the observed reduction in dsRNA production may be attributable reduction of backwards transcription (e.g., initiated upon hybridization with a polyA sequence such as the polyA tail).
[361] In some embodiments, a surprising reduction in dsRNA content compared to control (GTP fed) was observed when UTP was limited (Figure 1C). Furthermore, an opposing effect (e.g., an increase) was observed when ATP was limited (Figure 1C). Without wishing to be bound by any one theory, the observed increase in dsRNA content when limiting ATP was potentially due to a stalling of the T7 Polymerase at the end of the transcript, since not enough ATP may not have been present to synthesize a polyA tail at a typical speed (e.g., wherein ATP was not limited). This stalling might favor backward transcription due to longer residency of the Polymerase at the end of the transcript. An observed increase in dsRNA content when limiting ATP, was rescued (e.g., dsRNA content was reduced to control levels) by simultaneously feeding both ATP and UTP (Figure 1 C).
As mentioned above, the EMA pointed out that BioNTech (Pfizer) did not make any changes to the lower limit of the ATP concentration. From the disclosure in the para [361], it is understood that the reason for this is an increase in the dsRNA content due to poor formation of the polyA tail.
I could not understand the reason why the lower limit of CTP concentration was not changed, from this patent.
It is about time for BioNTech (Pfizer) to testify openly and in detail about everything, since BioNTech (Pfizer) has already admitted above matters. And this should be provided for further verification by a disinterested third party.
As mentioned above, BioNTech (Pfizer) made changes to increase the ATP and CTP concentrations early stage in the introduction of mRNA vaccine. With this change, BioNTech (Pfizer) reduced the amount of dsRNA contamination and increased the amount of residual plasmid DNA contamination.
Ideally, it would be desirable to reduce both of the amount of dsRNA contamination and the amount of residual plasmid DNA contamination at the same time, but BioNTech (Pfizer) prioritized reducing the dsRNA contamination.
Risks due to the dsRNA contamination and risks due to the residual plasmid DNA contamination are two separating issues and cannot be weighed against each other.
That is, no matter how we look at them, increasing the amount of DNA contamination tenfold in order to reduce the amount of dsRNA contamination to one-third is disproportionate, and therefore this barter is extremely unnatural.
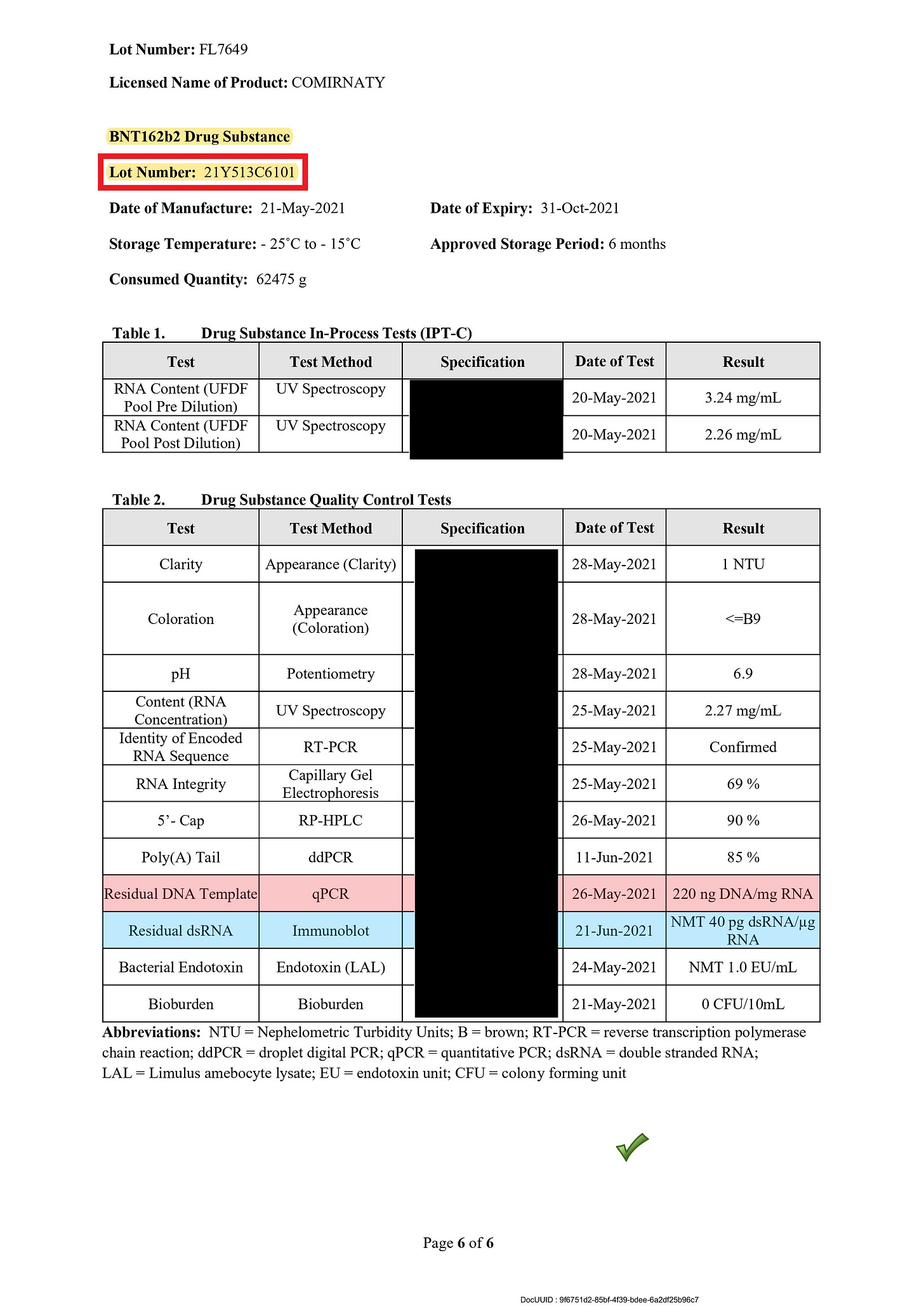
The amount of DNA contamination in a later Lot (21Y513C601) to the above Lot 21Y513C501 disclosed in the another TGA document (ref. 10) is 220ng, and it has not been improved. On the other hand, the amount of dsRNA contamination seems to be further improved.
This is an indication that BioNTech (Pfizer) wanted to reduce the amount of dsRNA contamination even at the expense of the residual plasmid DNA contamination, and at the same time is an evidence that BioNTech (Pfizer) took the risks of the dsRNA contamination seriously.
Throughout this pandemic, I have never heard from BioNTech (Pfizer) or any government official about the risks of the dsRNA contamination (and of course the risks of the DNA contamination). However, in the patents and the papers, the risks of the dsRNA contamination are openly disclosed as if it were a matter of course.
The matters (technologies and their risks) that are well known among experts are not necessarily well known among the public. Just as a company uses commercials to advertise the same product over and over again, it is necessary to present formal documents to the public many times in an easy-to-understand manner in order to make the technologies and their risks well known.
They have actively used the taglines "safe and effective," "compassionate," and "to protect your loved ones," but these taglines do not include the risks related to the dsRNA contamination and the DNA contamination. I never believe that informed consent has been achieved with the disclosures of the patents and papers.
Furthermore, in the Emergency Supply, etc., BioNTech (Pfizer) had introduced the mRNA vaccine into the human body that had the dsRNA contamination three times higher than the current level. And currently, BioNTech (Pfizer) has introduced the mRNA vaccine into the human body that has the DNA contamination 10 times higher than the prior level.
How is this "safe and effective? How was the risks to the human body caused by those contaminations evaluated? This is not matters that I should explain to the public, but rather matters that BioNTech (Pfizer) and government officials should explain to the public in good faith.
Experts exist to share their knowledges with the public and contribute to the development of industry. To develop specific technologies contributes to industrial development, but to identify the risks of specific technologies and eliminate them from society also contributes to industrial development.
However, with this mRNA vaccine platform, the technical information is hidden by pharmaceutical companies. This not only hinders verification of the actual harm caused by the mRNA vaccine, but also severely impedes industrial development.
Even worse, the government is complicit in this, working with pharmaceutical companies to build a fictitious industry. This kind of social structure is extremely distorted and seriously impedes healthy technological development and the healthy lives of the citizens.
I would like to conclude this post with a critique against BioNTech (Pfizer) and the government, which are extremely dishonest to the public.
Digression
In addition to the Table 5-1 of the patent disclosed this time, this patent discloses some tables that are consistent with the tables disclosed in the EMA document. Therefore, further knowledge will be able to be obtained by using this patent in conjunction with reading the EMA document.
This patent also discloses a phosphorothioate modified 5' cap in para [258] etc. This is a modification that increases the resistance to degradation by enzymes, and is the latest technology that differs from the disclosure in the EMA document.
[258] In some embodiments of the present invention, the RNA of the present invention comprises a phosphorothioate-cap-analog wherein the phosphorothioate modification of the RNA 5’-cap is combined with an “anti-reverse cap analog” (ARCA) modification. Respective ARCA-phosphorothioate-cap-analogs are described in WO 2008/157688 A2, and they can all be used in the RNA of the present invention. In that embodiment, at least one of R2 or R3 in Formula (1) is not OH, in some embodiments one among R2 and R3 is methoxy (OCH3), and the other one among R2 and R3 is in some embodiments OH. In some embodiments, an oxygen atom is substituted for a sulphur atom at the beta-phosphate group (so that R5 in Formula (I) is S; and R4 and R6 are O). It is believed that the phosphorothioate modification of the ARCA ensures that the a, p, and y phosphorothioate groups are precisely positioned within the active sites of cap-binding proteins in both the translational and decapping machinery. At least some of these analogs are essentially resistant to pyrophosphatase Dcpl/Dcp2. Phosphorothioate-modified ARCAs were described to have a much higher affinity for eIF4E than the corresponding ARCAs lacking a phosphorothioate group.
The review of this patent has not been completed yet, so I will update it as soon as I find out anything.
Thank you.
Cultivate 2
mbi
Patent SUN
Reference List
Ref. 1: My Post about US20230183769A1 (ATP and CTP concentrations)
(1) https://x.com/Patent_SUN/status/1753011648015835304
(2) https://image-ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/20230183769
(3) https://patents.google.com/patent/US20230183769A1/en?oq=US2023%2f0183769A1
(4)
Masterpiece of BioNTech & Pfizer
Regarding BioNTech patent US2023/0183769A1 I previously posted, which admittedly increases the residual DNA, I would like to emphasize another point here. Please compare the descriptions of the patent and the EMA document as reproduced below. The two documents say almost same thing, but ''something'' is missing from
Ref. 2: WO2022122689A1 (US20240110214A1)
(1) https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2022122689A1/en?oq=WO2022122689A1
(2) https://patents.google.com/patent/US20240110214A1/en?oq=US20240110214A1
(3) https://ppubs.uspto.gov/dirsearch-public/print/downloadPdf/20240110214
Ref. 3: EMA document
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1K-dWmwzH-gbsPstj3bTfYgS1DUTEqIn1uA2T5-4jZr0/edit
Ref. 4: A Facile Method for the Removal of dsRNA Contaminant from In Vitro-Transcribed mRNA (BioNTech, Katalin Karikó, et al.)
Ref. 5: WO2017182524A1 (Conflicts of Interest of ref. 4)
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2017182524A1/en?oq=2017%2f182524
Ref. 6: Template Strand Switching by T7 RNA Polymerase
https://www.jbc.org/action/showPdf?pii=S0021-9258%2818%2944732-1
Ref. 7: TGA document
https://www.tga.gov.au/sites/default/files/foi-3471-01.pdf
Ref. 8: Anandamide substack (from Mr. McKernan)
(1)
(2)
Ref. 9: My post about PrionGate
https://x.com/Patent_SUN/status/1699619448909713661
Ref. 10: Another TGA document
https://www.tga.gov.au/sites/default/files/foi-3390-11.pdf
























I can only roughly understand it, but I think it's a great job.
An expert only in genetic engineering probably wouldn't notice the medical risks, and an average doctor wouldn't even have the idea to search for the patent itself. Molecular biologists can search for papers, but they won't be able to search for patents the way you can.
I hope Dr. Hiroshi Arakawa of the Institute of Molecular Oncology in Milano realizes this.
Sorry I missed this great analysis you published in May 2024 and have now added it as a key reference to my short article on the same subject of dsRNA.
https://geoffpain.substack.com/p/picograms-of-double-stranded-rna